When it comes to either pain or performance issues, we’re often told that we need to get stronger. We need to strengthen our core to help back pain. We need to strengthen our legs to pedal or run faster. We need stronger arms to swim better. Strength is important for sure. There’s no substitute for it. It’s money in the bank.
Awareness and pain
Here’s something slightly different to consider: Awareness. A lot of pain and poor performance issues aren’t so much strength-related as they are awareness-related. By this I mean we need to know how to use our muscles to control our limbs and a lot of us don’t have the awareness we need to accomplish the task. Here’s a common example:
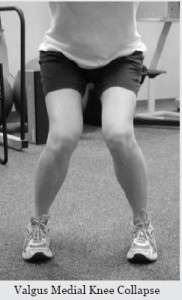
A client complains of knee pain. I watch them squat, walk up and down stairs, and maybe do some one-leg mini-squats.
I observe a valgus collapse–the knee or knees cave in as he or she moves.
What are the consequences?
This type of movement pattern sets us up for knee ligament damage, meniscus damage, IT band pain, patella pain, and possibly back pain. Even if the person isn’t in pain, this is a very inefficient movement pattern. Whether running or walking, this valgus pattern makes for poor shock absorption and energy transfer into the ground. We’re slow and weak when our knees collapse like this.
Why is it happening?
Back to the “A” word, awareness. Very commonly we can’t use our glutes correctly–and we’re not aware that we’re not using them. We have what Thomas Hanna calls “sensory motor amnesia.” We’ve forgotten how to move. (Modern living is a killer. We sit too much!!)
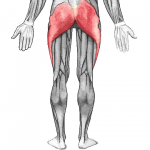
Why do glutes matter to knees?
The glutes (glute maximus, medius and minimus) along with the tensor fasciae latae start up in the pelvis and feed into the IT band. The IT band then attaches to the top of the tibia right below the knee. In this arrangement, if we tighten or squeeze the glutes the knee will rotate outwards. If we release tension from the glutes then the knee will tend to collapse in. Control of the knee largely resides at the hip with the glutes. (By the way, we could discuss awareness of the foot as it pertains to a valgus knee too. If the big toe isn’t firm to the ground and we don’t have competent arches then the knee may collapse in.)
What’s the solution?
Often someone with knee pain has been told they need to strengthen muscles around the knees namely the quadriceps. This was the thinking for years. So people did knee extensions. The muscles near the knee definitely got stronger but that didn’t improve the walking, running, or stepping pattern that was causing the pain. Now we understand that the glutes have more influence over the knee than the muscles surrounding the knee. The pattern of movement is the key factor. It’s how we use our muscles! We must become aware of how we move, and aware of how we employ our muscles during movement. If we gain awareness of the glutes then we can start to control the knee. Strength isn’t the main issue. (The same can be said for the deep core muscles and back pain.)
We need awareness before we can get strong, fast or powerful. In fact, if we’re not moving well–if we’re not aware of how we’re moving–and we add weight or speed to the scenario then we’re marching headlong into dysfunction, pain, and poor performance. It’s analogous to hammering a bent nail. The harder we pound the more it bends and we’re headed for trouble.
Awareness for performance: the bench press
I spoke with a friend and former client of mine who’s learning to bench press. (My ego demands that I tell you he lives in another state which is why he’s working with a different trainer.) He told me he learned to use his lats for the bench press. (Think of trying to bend the bar into a horseshoe.) Now, with the lats engaged he’s got a stronger foundation from which to press. He’s called in more muscles to help disperse the work. His shoulders are more stable. Now he can get stronger and likely avoid injury. Awareness should come first. (I wish I were aware of all this stuff when I was training him!)
Beyond this example, Louie Simmons in the Westside Barbell Squat and Deadlift Manual directs lifters to identify their weakness–become aware of them in other words–and work to shore them up. He says don’t necessarily do the exercises you like. Do the exercises that work for you.
Awareness for performance: running
First, all the stuff above about glutes and knees pertains very much to running. Remember that. What else should we be aware of while running? Think about where your foot lands. Does it land way out in front? It shouldn’t. If it does you’ll likely have problems. Rather, the foot should land just barely out in front of your center of mass and the foot should land right below the knee, not out in front. If you watch recreational runners you’ll often see the foot land out in front. Watch elite runners and that foot lands very close to right underneath. Think of your leg as a swinging pendulum. If the pendulum swings wide then a) your foot lands out in front, b) your cadence is slower and c) it’ll take more energy to run. In a better situation you’ll swing your pendulum/leg in a shorter arc. The foot will land closer to you which will result in a faster cadence and you’ll be more efficient. You’ll be faster and you’ll be in a better position to avoid injury. For more on this and further awareness of how you should run, check out this very informative article by Jay Dicharry, author of Anatomy for Runners.
Awareness for weight loss
So we’ve discussed awareness as it pertains to pain and performance. Where else does it matter? Do you want to get leaner and generally healthier? Then you better be aware of your eating habits. Very similar to poor movement patterns, poor eating habits will over the course of time do great damage to our physique and overall health. The problem is a habit is an unconscious thing. We’re not aware of our habits! We eat mindlessly in front of the TV. We’re caught without healthy food to eat so we resort to fast food or packaged frozen dinners. We take nibbles of junk snacks thinking that we’re not eating that much garbage, but by the end of the week we’ve consumed a lot of crapola. The result? We look and feel like a sick, sluggish mess. What can we do?
Keeping a food journal is by far one of the most effective and cheapest things you can do to help become aware of your eating habits. You can use any notebook. Or you can use an online program such as MyFitnessPal.com.
Does this sound inconvenient? Writing out 1/2 cups, tablespoons, grams, etc. can be a hassle. Guess what. You don’t have to employ painstaking detail to get the benefits of keeping a food journal. You don’t even have to track every meal every day. If you eat some M&Ms, write “M&Ms.” If you eat a salad write “salad.” If you can only manage to track breakfast three days a week then that’s better than tracking nothing at all. The point is to start to become aware of your eating habits. Any progress at all is progress. Awareness must come before you can expect to see change.
Awareness elsewhere in life
How are you handling stress? What time do you go to bed? If you’re trying to get in shape or you’re training to compete, you better know these things. If you’re aware of your workouts but your not aware of how you’re resting then you’re compromising your ability to lose weight and compete.
Hard exercise is stress. So is work. So are some of our interpersonal relationships. Alcohol and sugary foods cause stress. The winter holidays are full of stressors. If stress goes up in one or more areas then it must come down in others. Otherwise you’re courting illness, injury or at the very least extreme fatigue. If you’re feeling pulled in 100 directions then it may be a good idea to scale back your workouts a little. Don’t give up though! Recognize that more/harder exercise won’t help you if you’re highly stressed. Finding some way to decrease some of your stress is critical to good mental and physical health. Take stock of these things. Be aware of what’s going on in your life. Then you can take measures to manage things.