In the previous post, I discussed a few thoughts, ideas and myths surrounding our posture. A key concept is that posture actually isn’t tied very strongly to back pain. There are still good reasons to learn and practice good posture though.
Proper posture while lifting
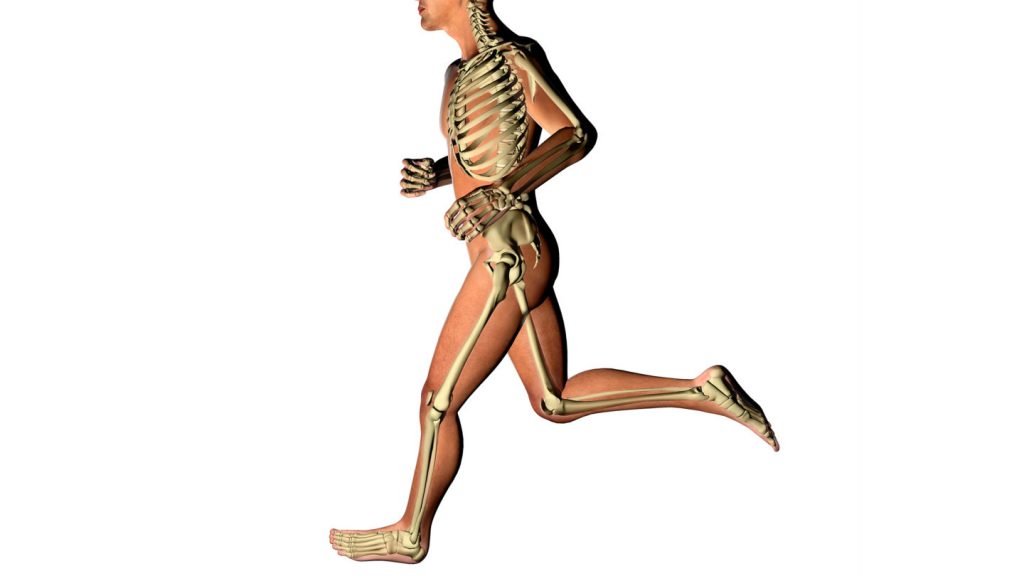
Let’s think of a squat or deadlift. In these exercises, the legs are the engines that drive the exercise. They provide the “oomph” to move the barbell (or whatever implement) we’re holding in your arms/hands. The trunk is the transmission between the engines and the arms/hands/object.

The deadlift done wrong (left) and well (right.)
Keeping the spine braced in a neutral position ensures the best, most efficient transfer of force from the legs into the barbell. If the spine twists or bends then we leak force and risk injury.
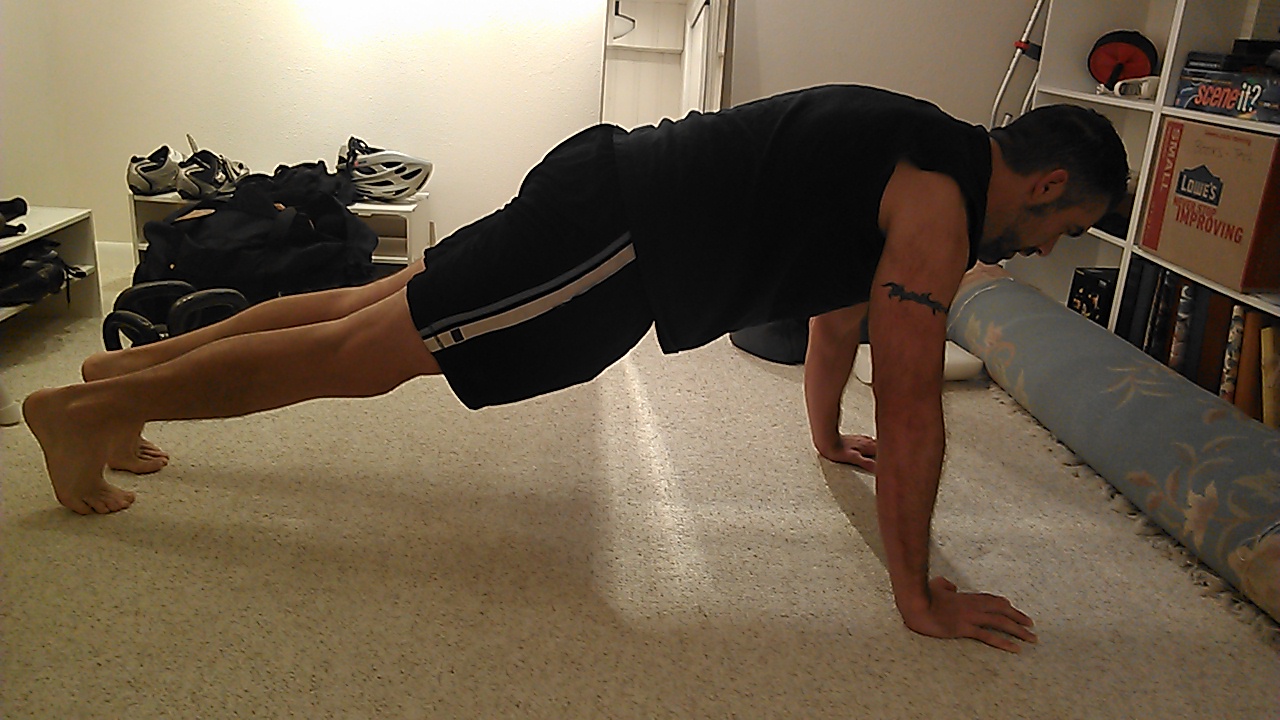

Glutes, abs and shoulder muscles are engaged. Keep it this way during a push-up.
Similarly, look at a push-up. Here, the arms and the shoulders are the drivers and the rest of the body is the implement we’re moving. We again want to keep the trunk rigid and braced, not loose, deflated and floppy. With proper technique we get a more thorough range of motion and stimulate the working muscles more. By doing a push-up in good posture, you’ll essentially get more out of the exercise than if you do it with poor posture. Risk of shoulder and back injury is reduced too.
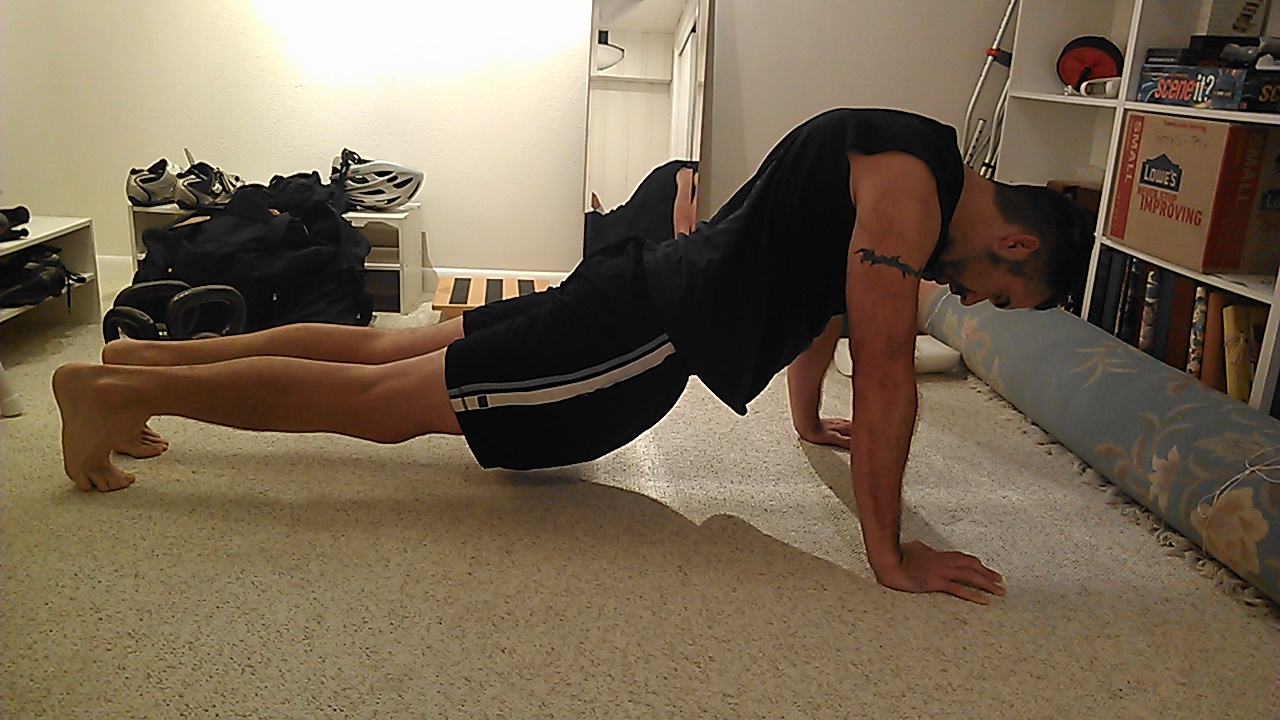
Bad push-up! No!
We can expand our view of posture out to any number of sports from running to golf to tennis to whatever else you like. In the vast majority of our sports, we want to keep solid posture so we can most effectively transmit force (usually) into the ground and into something like a club, a ball or an opponent.
In the grand scheme, good solid posture will enable you to lift more weight which will enable you to reach your fitness goals faster and more effectively. We can also make our sporting movements more effective through the use of good posture. You’ll avoid injury too which will allow you to train longer and more consistently.
Posture and safety.
Okay, in the last post, I mentioned that pain isn’t strongly linked to posture. Yet in this post (above) I’ve suggested that braced, neutral posture while lifting can help prevent injury. Am I contradicting myself? Not entirely.
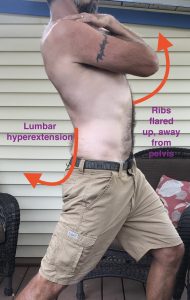
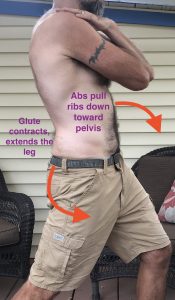
If we load our joints at the far ends of where they can move then we do risk doing damage to joint tissues and this may bring on pain. So we want to avoid excessive spinal flexion, and/or spinal extension, and/or spinal twisting when lifting. Yes our spine can and should bend and twist, just not under heavy load. Rather we should put the spine in neutral and brace with the trunk muscles before we lift.
Posture for looks
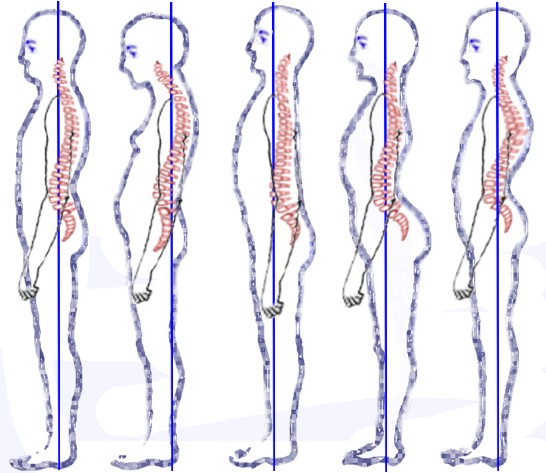
Why do most people work out? Looks, no? For most of us, looks is somewhere on our list of reasons we exercise. We want to look lean and strong. Adopting good, erect, tall posture will instantaneously improve our appearance. Incredible! Tall posture makes us appear leaner and stronger. Slumped posture makes us look pudgy and weak. Look at the pictures and you be the judge.
(Ironically, when I look around the gym, I see lots of people exercising in very bad posture. Presumably they want good looks yet they engage in activities that only reinforce bad posture. Crunches may be the most effective way of promoting slumped, head-forward-style bad posture.)
Posture and confidence — (Yes posture and the brain are linked!)
Power Posture!
The same tall posture described above makes you feel better and more confident. Don’t believe me?

He looks like a leader.
Here’s the abstract from a study looking at this phenomenon (emphasis is mine.):
“Building on the notion of embodied attitudes, we examined how body postures can influence self-evaluations by affecting thought confidence, a meta-cognitive process. Specifically, participants were asked to think about and write down their best or worse qualities while they were sitting down with their back erect and pushing their chest out (confident posture) or slouched forward with their back curved (doubtful posture). Then, participants completed a number of measures and reported their self-evaluations. In line with the self-validation hypothesis, we predicted and found that the effect of the direction of thoughts (positive/negative) on self-related attitudes was significantly greater when participants wrote their thoughts in the confident than in the doubtful posture. These postures did not influence the number or quality of thoughts listed, but did have an impact on the confidence with which people held their thoughts.”
Here’s an excerpt from an article in Scientific American on the same subject:
“More impressively, expansive postures also altered the participants’ hormone levels. Using salivary samples, Carney and colleagues found that expansive postures led individuals to experience elevated testosterone (T) and decreased cortisol (C). This neuroendocrine profile of High T and Low C has been consistently linked to such outcomes as disease resistance and leadership abilities.”
and
“Together, these recent discoveries bolster the notion that power is grounded in the body. Not only does power change the body, but altering one’s postures changes one’s power, or at least the psychological experience of it.”
Finally, for a little more about the power of posture, here’s Amy Cuddy discussing the topic in a TED Talk: