I’ve recently mentioned California-based physical therapist Kelly Starrett, and his very interesting blog MobilityWOD.com. (I’m doing his Mobility Course in Denver at the end of April.) One of his posts discusses why sitting is poison for your ability to move. (Also, check out Why sitting all day is slowly killing you for more details on this evil activity.) He’s on to something. Sitting is bad and we need to do something about it.
You sit too much.
By the way, if you’re saying, “But I don’t sit that much,” I have several questions for you:
1) Are you a non-Amish/non-lumberjack American in the modern world? If you say “yes” then you sit too much.
2) Do you own a car? If you say “yes” then you sit too much.
3) Is there a desk and/or a computer involved in your life? Clearly your answer is “yes” because you’re reading this.
4) Are you a cyclist? If it’s “yes” then you sit too much.
5) You sit too much.
Effects of sitting
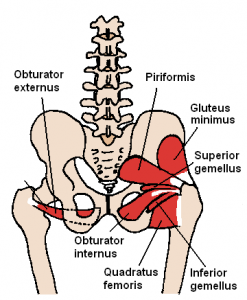
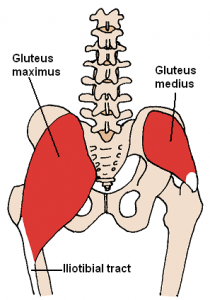
So what does sitting do to us? First, we get restrictions in a bunch of our muscles and tissues. Particularly we see restrictions in our posterior hip capsule. This type of restriction can contribute to a condition called anterior femoral glide syndrome, which can cause pain at the front of the hip and generally bad movement. Further, the various
muscles in this region can become impaired, tight and weak. Sitting shuts down these muscles and our brain literally forgets how to use these extremely important movers and stabilizers. All of this can result in various aches and pains, poor balance, difficulty sitting and standing, poor running form, poor lifting form–it’s all bad!! What’s the solution?
Mobilize & strengthen
The best way to address these restrictions is to move. We’ve got to move the tight tissues and we have to re-learn how to operate these muscles that have likely gone dormant. What follows are three drills borrowed and adapted from Shirley Sahrmann and Nick Tumminello.
Simply doing these movements and feeling a stretch in the hip will help loosen tight tissue, but we want to go beyond that. Again, we need to re-learn how to use these muscles and in order to do that you must contract them as you’re doing these drills. Think of adjusting the tension of your glutes in much the same way as you’d adjust the tension of your bicep during a bicep curl. You’ll maintain tension throughout the movement even as the muscle become stretched. You’ll probably
find it difficult to maintain a perceptible contraction as the glute stretch. Work on it. It’s a skill that you should develop in order to overcome pain and perform better. It’ll take practice but the payoff will be tremendous.